Cryostate
The 77 K frontier in FT-IR adsorption experiments on high surface area powdered materials has been broken down
very recently, thanks to the realization in our laboratory of an unique experimental set-up able to perform
FT-IR experiments in transmission mode down to 15 K on materials activated in situ under vacuum conditions
(P < 10-4 Torr) and at temperatures up to 1100 K.
Research guideline
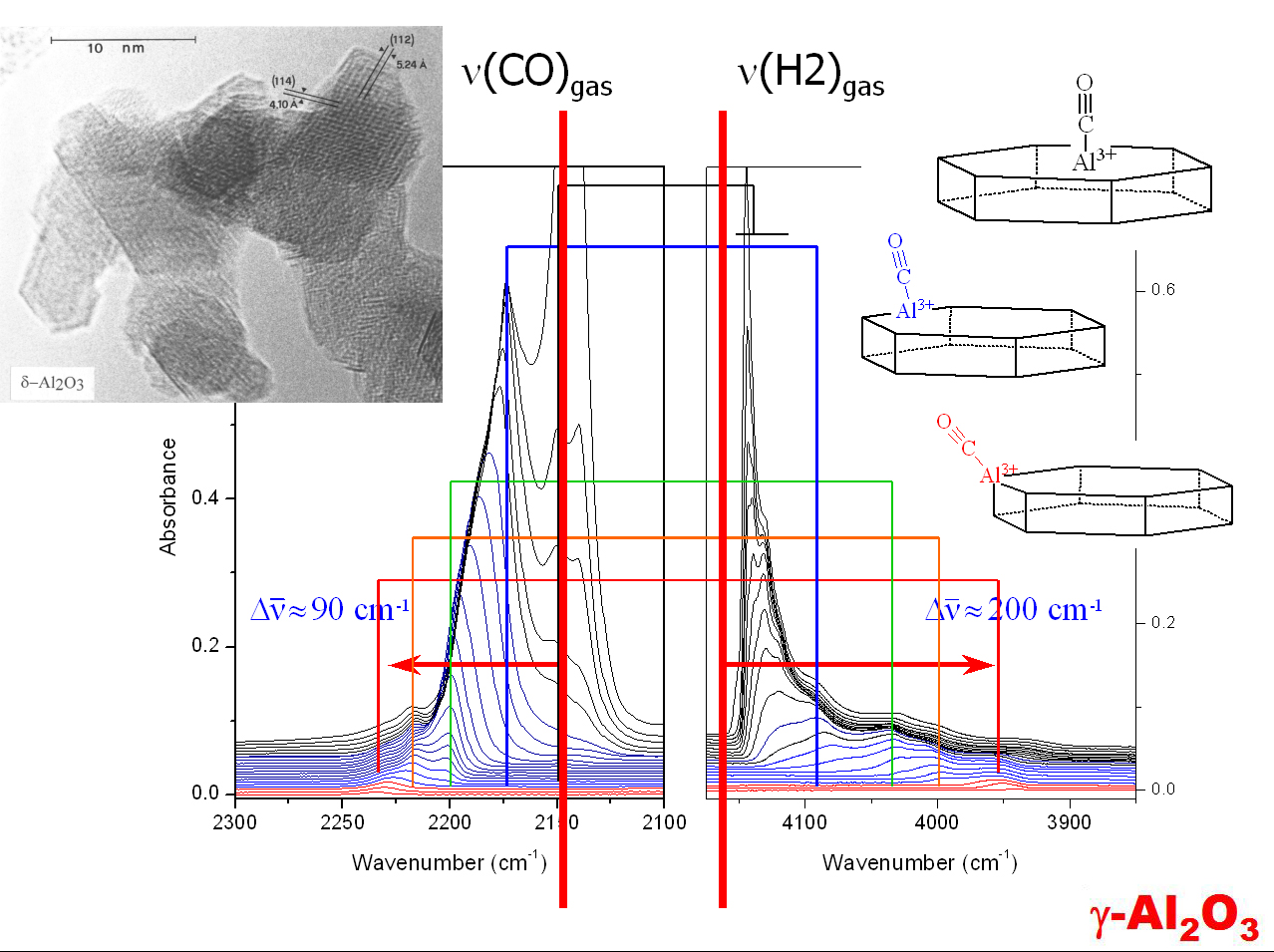
- Effect of the temperature on the vibrational properties of surface species
- IR spectroscopy of probe molecules (H2, CO, ... ) in order to characterize the properties of surfase sites.
- Adsorbion enthalpy of surface sites toward adsorbed probes (H2, CO, ... )
Equipment
In order to perform in situ measurement at temperature variable in the 20–300 K range, a Bruker Equinox-55 FTIR spectrometer
has been modified with an apparatus built ad hoc. It can be divided into three parts:
- The cryogenic part, which consists of cryogenic head where a de-fined temperature can be set in the 20–300 K range exploiting
a commercial cryostat apparatus
- The activation part, where the sample can be heated either in high vacuum conditions (P < 10-3 Torr: 1Torr < 133.3 Pa)
or in the desired atmosphere up to 1073 K. A magnetic manipulator allows us to move the sample holder from the oven to the cryogenic
cell under high vacuum conditions
- The vacuum system, which allows to maintain the dynamical vacuum during the activation procedure as well as to dose the desired
amount of the probe gas on the sample maintained at the desired temperature and to reduce (or increase)
progressively the coverage
At each state of the experiment, the equilibrium pressure is monitored in the different parts of the instrument using both Pirani
and membrane gauges. The cryogenic cell, equipped with four IR transparent windows, is hosted inside spectrometer allowing the IR
beam to pass through the activated sample for transmission measurements.
Research guideline
- Effect of the temperature on the vibrational properties of surface species
- IR spectroscopy of probe molecules (H2, CO, ... ) in order to characterize the properties of surfase sites.
- Adsorbion enthalpy of surface sites toward adsorbed probes (H2, CO, ... )